What Is Heel Pain And The Right Way To Alleviate It
Overview
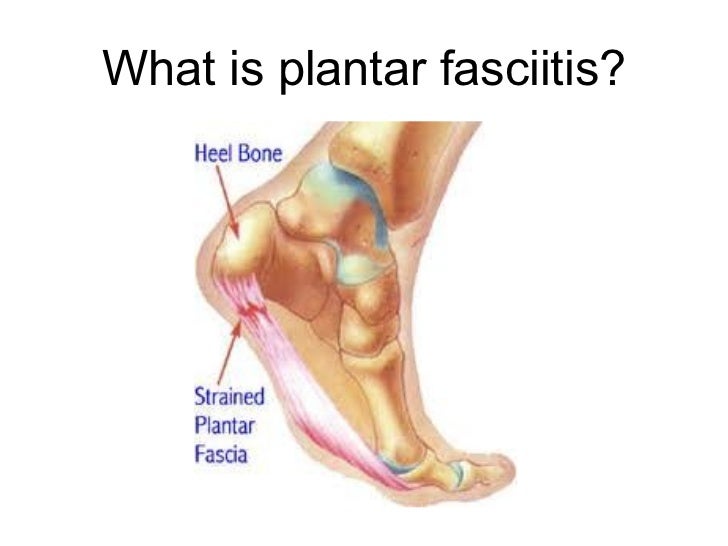
Plantar fasciitis, also called “heel pain syndrome,” affects approximately 2 million people in the United States each year. Plantar fasciitis can come on gradually as the result of a degenerative process or sudden foot trauma. It can appear in one heel or both. It is generally worse on taking the first few steps in the morning or after prolonged sitting or non-weight-bearing movement. Symptoms can be aggravated by activity and prolonged weight bearing. Obesity, too, is hard on the feet-it can cause plantar pain or it can make that pain worse. The plantar fascia connects the calcaneal tubercle to the forefoot with five slips directed to each toe respectively. Other conditions, such as calcaneal fat pad atrophy, calcaneal stress fracture, nerve entrapment, and rheumatoid arthritis may also cause foot pain. These conditions may be found in combination with plantar fasciitis, or separate from it. A blood test can help pinpoint the cause(s).
Causes
Plantar fasciitis is usually not the result of a single event but more commonly the result of a history of repetitive micro trauma combined with a biomechanical deficiency of the foot. Arthritic changes and metabolic factors may also playa part in this injury but are unlikely in a young athletic population. The final cause of plantar fasciitis is "training errors." In all likelihood the injury is the result of a combination of biomechanical deficiencies and training errors. Training errors are responsible for up to 60% of all athletic injuries (Ambrosius 1992). The most frequent training error seen with plantar fasciitis is a rapid increase in volume (miles or time run) or intensity (pace and/or decreased recovery). Training on improper surfaces, a highly crowned road, excessive track work in spiked shoes, plyometrics on hard runways or steep hill running, can compromise the plantar fascia past elastic limits. A final training error seen in athletics is with a rapid return to some preconceived fitness level. Remembering what one did "last season" while forgetting the necessity of preparatory work is part of the recipe for injury. Metabolic and arthritic changes are a less likely cause of plantar fasciitis among athletes. Bilateral foot pain may indicate a metabolic or systemic problem. The definitive diagnosis in this case is done by a professional with blood tests and possibly x-rays.
Symptoms
The symptoms of plantar fasciitis include pain in the bottom of your foot, especially at the front or centre of the heel bone, pain that is worse when first rising in the morning (called "first-step pain"), when first standing up after any long period of sitting, or after increased levels of activity especially in non-supportive shoes. Seek medical advice about plantar fasciitis if you have heel pain or pain in the bottom of your foot, especially when you get up in the morning, that does not respond to treatment or if there is redness or bruising in the heel.
Diagnosis
After you describe your symptoms and discuss your concerns, your doctor will examine your foot. Your doctor will look for these signs. A high arch, an area of maximum tenderness on the bottom of your foot, just in front of your heel bone. Pain that gets worse when you flex your foot and the doctor pushes on the plantar fascia. The pain improves when you point your toes down. Limited "up" motion of your ankle. Your doctor may order imaging tests to help make sure your heel pain is caused by plantar fasciitis and not another problem. X-rays provide clear images of bones. They are useful in ruling out other causes of heel pain, such as fractures or arthritis. Heel spurs can be seen on an x-ray. Other imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound, are not routinely used to diagnose plantar fasciitis. They are rarely ordered. An MRI scan may be used if the heel pain is not relieved by initial treatment methods.
Non Surgical Treatment
Conservative treatment is almost always successful, given enough time. Traditional treatment often includes, rest, NSAIDs, and new shoes or heel inserts. Some doctors also recommend avoiding walking bare-footed. This means you’d have to wear your shoes as soon as you wake up. Certain foot and calf exercises are often prescribed to slowly build strength in the ligaments and muscles that support the arch of the foot. While traditional treatment usually relieves pain, it can last from several months to 2 years before symptoms get better. On average, non-Airrosti patients tend to get better in about 9 months.

Surgical Treatment
Most practitioners agree that treatment for plantar fasciitis is a slow process. Most cases resolve within a year. If these more conservative measures don't provide relief after this time, your doctor may suggest other treatment. In such cases, or if your heel pain is truly debilitating and interfering with normal activity, your doctor may discuss surgical options with you. The most common surgery for plantar fasciitis is called a plantar fascia release and involves releasing a portion of the plantar fascia from the heel bone. A plantar fascia release can be performed through a regular incision or as endoscopic surgery, where a tiny incision allows a miniature scope to be inserted and surgery to be performed. About one in 20 patients with plantar fasciitis will need surgery. As with any surgery, there is still some chance that you will continue to have pain afterwards.